ADVERTISEMENT
The distribution of body fat is a topic of great interest and importance, as it can reveal significant information about an individual’s health status and lifestyle. The way our bodies store fat varies greatly between individuals and can be influenced by factors such as genetics, hormones, and diet. Understanding these patterns is crucial because certain types of fat distribution are associated with higher risks for various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
In recent years, advancements in medical research have provided us with greater insights into the implications of fat distribution. For instance, visceral fat stored in the abdominal cavity has been shown to be more harmful than subcutaneous fat, which lies just beneath the skin. The significance of body fat location goes beyond aesthetics; it’s a matter of health and longevity. Knowing where your body tends to store fat can empower you to make more informed health decisions and adopt strategies that are specifically tailored to combat the risks associated with these fat deposits.
Advertisement
1. Upper Body Fat (Apple Shape):
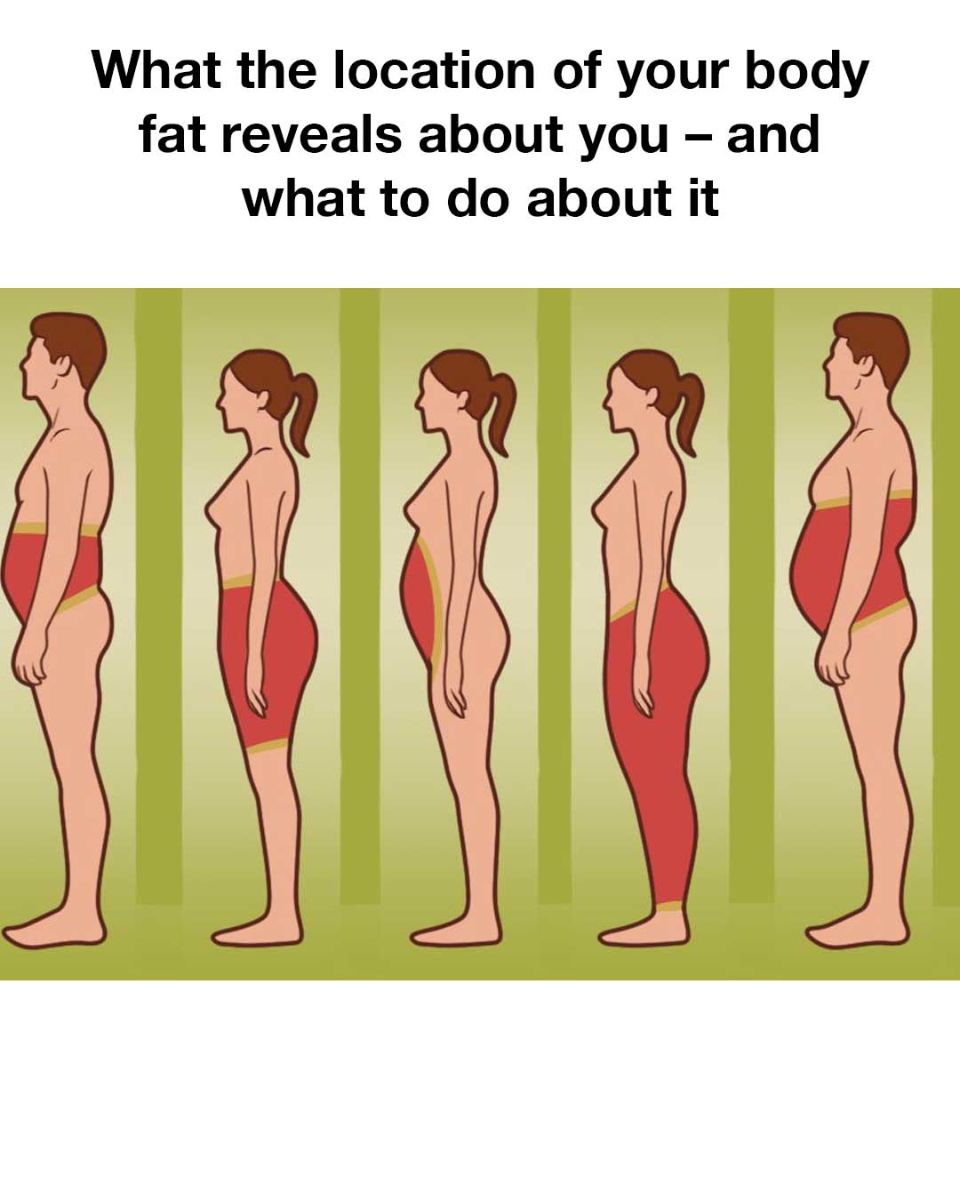
People who store most of their fat in the upper body, particularly around the abdomen, chest, and back, are often described as having an “apple shape.” This type of fat distribution is linked to higher levels of visceral fat, which can encase vital organs and lead to serious health issues such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Individuals with this fat distribution should focus on a combination of cardiovascular exercises, strength training, and a diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats to reduce abdominal fat.
2. Lower Body Fat (Pear Shape):
Those who carry extra weight in their hips, thighs, and buttocks tend to have a “pear shape.” While this type of fat distribution is generally considered to be less risky than upper body fat, it can still lead to complications such as varicose veins and joint problems. To manage lower body fat, individuals should incorporate a mix of aerobic exercises, leg-focused strength training routines, and a balanced diet to help reduce fat in these regions.
3. Total Body Fat (Overweight/Obese):
When fat is distributed evenly throughout the body, it often indicates a general state of being overweight or obese. This scenario raises the overall risk for a variety of health issues, as excess fat can affect virtually every organ system. A comprehensive approach that includes calorie monitoring, regular physical activity, behavioral therapy, and, in some cases, medical interventions or weight loss programs is necessary to address this type of fat distribution.
4. Visceral Fat:
For Complete Cooking STEPS Please Head On Over To Next Page Or Open button (>) and don’t forget to SHARE with your Facebook friends
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT